acl mcl tear test|mcl acl tear recovery time : department Store ACL vs. MCL tears: Although symptoms of ACL and MCL tears are similar, a few key differences will help identify whether the injury affected the ACL or MCL. An ACL tear will have a more distinctive and loud popping sound than an MCL tear. When used properly, autoclaves are safe and highly effective. Autoclaves use saturated steam under pressure of approximately 15 pounds per square inch to achieve a .HEPA filters are designed to target tiny pollutants and particles as small as viruses that can be 10X smaller than standard bacteria. The particles are trapped through a combination of mechanisms called interception, impaction and diffusion. A detailed discussion of how each mechanism works is beyond the scope of . See more
{plog:ftitle_list}
Dry saturated steam at high pressure when strikes the cooler surfaces of the articles in the autoclave, condenses into water, and efficiently destroys all microorganisms along with thermal-resistant bacterial spores.Combine compact design with high performance, reliability and safety. Intelligent design for your professional choice. Printer not included. Spot an opportunity for improvement?

ACL vs. MCL tears: Although symptoms of ACL and MCL tears are similar, a few key differences will help identify whether the injury affected the ACL or MCL. An ACL tear will . Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Lacchman’s test. It is performed with the patient supine and the knee flexed 20–30°. The examiner grasps the distal femur (from lateral side) with one hand and the proximal tibia with the other hand (from medial side). The lower leg is given a brisk forward tug in an attempt to identify a discrete endpoint. ACL vs. MCL tears: Although symptoms of ACL and MCL tears are similar, a few key differences will help identify whether the injury affected the ACL or MCL. An ACL tear will have a more distinctive and loud popping sound than an MCL tear. An MRI can show the extent of an ACL injury and signs of damage to other tissues in the knee, including the cartilage. Ultrasound. Using sound waves to visualize internal structures, ultrasound may be used to check for injuries in the ligaments, tendons and muscles of .
An MCL tear is damage to the medial collateral ligament, which is a major ligament that’s located on the inner side of your knee. The tear can be partial (some fibers in the ligament are torn) or complete (the ligament is torn into two pieces). ACL tears are common athletic injuries leading to anterior and lateral rotatory instability of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee effusion with increased laxity on Lachman's test but requires MRI studies to confirm diagnosis. What causes ACL tears? Anything that puts too much force on your knee can tear your ACL. ACL tears happen when your knee moves or twists more than it naturally can. The most common causes of ACL tears include: Sports injuries. Car accidents. Falls. ACL tear risk factors. Anyone can experience an ACL tear.A medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury is a stretch, partial tear, or complete tear of the ligament on the inside of the knee. A valgus trauma or external tibia rotation are the causes of this injury.
A medial collateral ligament (MCL) knee injury is a traumatic knee injury that typically occurs as a result of a sudden valgus force to the lateral aspect of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected with increased valgus laxity on physical exam but requires MRI for confirmation. Treatment is generally nonoperative with bracing. Two of the most frequently encountered knee injuries are tears of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the medial collateral ligament (MCL). While both injuries involve ligament damage and can result in pain and instability, they differ in their causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
worst NBA injuries acl mcl
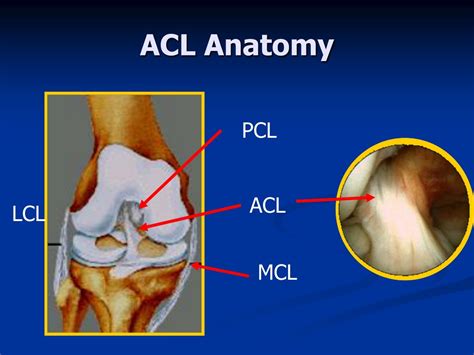
anterior cruciate ligament. ( ACL. ), posterior cruciate ligament. ( PCL. ), medial collateral ligament. ( MCL. ), and. lateral collateral ligament. ( LCL. ) result in knee pain and instability. Various maneuvers can be used to evaluate the stability of the joint and usually suffice to diagnose collateral. ligament. tears. An. MRI. is the best. Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Lacchman’s test. It is performed with the patient supine and the knee flexed 20–30°. The examiner grasps the distal femur (from lateral side) with one hand and the proximal tibia with the other hand (from medial side). The lower leg is given a brisk forward tug in an attempt to identify a discrete endpoint. ACL vs. MCL tears: Although symptoms of ACL and MCL tears are similar, a few key differences will help identify whether the injury affected the ACL or MCL. An ACL tear will have a more distinctive and loud popping sound than an MCL tear. An MRI can show the extent of an ACL injury and signs of damage to other tissues in the knee, including the cartilage. Ultrasound. Using sound waves to visualize internal structures, ultrasound may be used to check for injuries in the ligaments, tendons and muscles of .
An MCL tear is damage to the medial collateral ligament, which is a major ligament that’s located on the inner side of your knee. The tear can be partial (some fibers in the ligament are torn) or complete (the ligament is torn into two pieces). ACL tears are common athletic injuries leading to anterior and lateral rotatory instability of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee effusion with increased laxity on Lachman's test but requires MRI studies to confirm diagnosis.
What causes ACL tears? Anything that puts too much force on your knee can tear your ACL. ACL tears happen when your knee moves or twists more than it naturally can. The most common causes of ACL tears include: Sports injuries. Car accidents. Falls. ACL tear risk factors. Anyone can experience an ACL tear.A medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury is a stretch, partial tear, or complete tear of the ligament on the inside of the knee. A valgus trauma or external tibia rotation are the causes of this injury. A medial collateral ligament (MCL) knee injury is a traumatic knee injury that typically occurs as a result of a sudden valgus force to the lateral aspect of the knee. Diagnosis can be suspected with increased valgus laxity on physical exam but requires MRI for confirmation. Treatment is generally nonoperative with bracing.
Two of the most frequently encountered knee injuries are tears of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and the medial collateral ligament (MCL). While both injuries involve ligament damage and can result in pain and instability, they differ in their causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
where is my acl located
what worse mcl or meniscus
mcl acl tear recovery time
For the safety of staff and patients alike, every dental practice must maintain impeccable sterilisation standards. Because of this, the efficacy and reliability of sterilisation equipment is key to how well your dental practice runs. There is .
acl mcl tear test|mcl acl tear recovery time